Development of the World’s Highest Performance Automotive Ultra-High Strength Steel Sheet
With the aim of developing the world’s highest performance ultra-high strength steel sheets for automotive use, ISMA targeted laboratory-level development of a steel sheet having tensile strength of 1.5 GPa, which is 2.5 times larger than that of the conventional steel (590 MPa class steel sheet) and elongation of 20 %, which is equal to that of the conventional material, while avoiding the use of rare metals as far as possible, by utilizing inexpensive carbon. As a result, the final target was achieved in FY 2017.
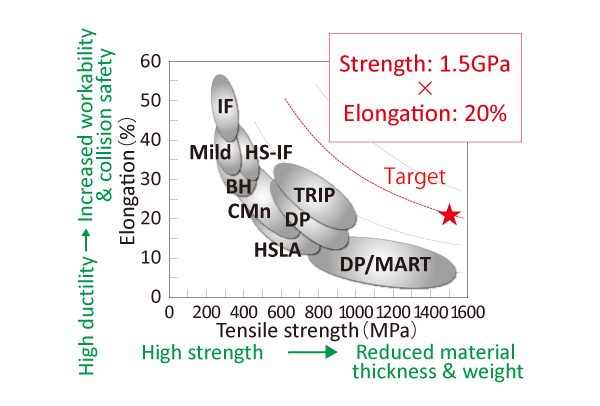
Final target of material performance

Automatic particle analysis system which accelerates analysis and evaluation of material fracture behavior
Research Achievements
Development of Innovative Steel Sheet by Advanced Control of Retained γ
Research Achievements
Two new types of innovative steel sheets were developed. Type A maximizes elongation by maximizing retained austenite (γ), and Type B features balanced formability, which is achieved by a combination of control of retained γ and refinement of the metallic microstructure.
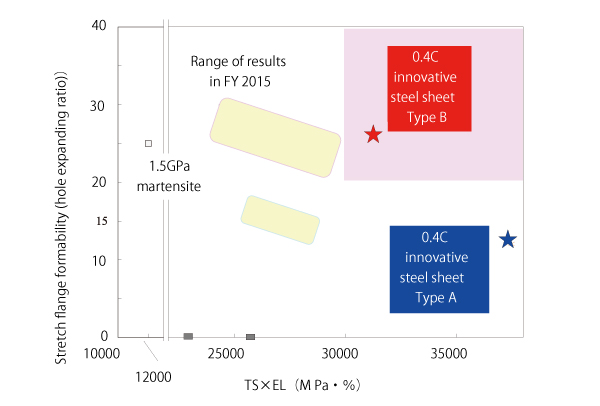
Improvement of balance of strength, elongation, and stretch flange formability by advanced control of retained γ
Development of Innovative Steel Sheet by Effective Utilization of Light Elements
Research Achievements
Microstructure control was performed to obtain a fine-grained martensite structure by composition design in which light elements were added to a base high carbon steel and optimization of rolling and heat treatment conditions. The fine-grained structure dramatically improved elongation in comparison with the existing high carbon steel.
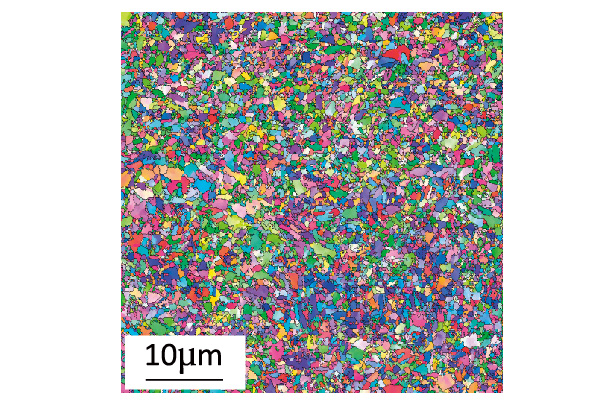
Refinement of martensite structure by effective utilization of light elements
Development of Ultra-High Strength Steel Sheet with Revolutionary Formability by Utilizing Carbon
Research Achievements
A technology for achieving ultra-high ductility in 1.2 GPa grade high strength steel sheets was established by FY 2015 by utilizing inexpensive carbon and uniform dispersion of fine austenite in the steels. The final target of tensile strength of 1.5 GPa and elongation of 20 % was realized by optimizing the chemical composition and heat treatment conditions. (Completed in FY2017)
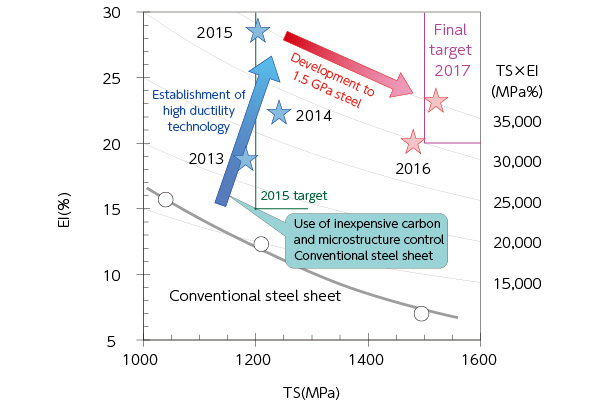
Satisfaction of both strength and ductility by use of carbon and microstructure control
